todays current affairs 29th july 2023

FOREX Reserves
GS Paper III (Economy)
Context: At $578.4 billion as of March 2023, India's foreign exchange reserves have decreased by over $28 billion from March 2022, $19.7 billion of which, according to the RBI, was attributable to value adjustments. The US dollar's decline in value and rising capital inflows were major factors in this year's climb in reserves.

What is Foreign Exchange (Forex) Reserve?
Important assets kept by the central bank in foreign currencies as reserves are known as foreign exchange reserves.
They are frequently employed to establish monetary policy and sustain the currency rate.
In the case of India, foreign reserves consist of gold, dollars, and a certain amount of SDRs from the IMF.
Given the currency's significance in the global financial and trade system, the majority of reserves are typically stored in US dollars.
In addition to holding reserves in US dollars, several central banks also hold reserves in Chinese yuan, British pounds, Japanese yen, and euros.
India’s forex reserves cover:
Foreign Currency Assets (FCAs)
Special Drawing Rights (SDRs)
Gold Reserves
Reserve position with the International Monetary Fund (IMF)
Current Scenario: Impact of US Rate Hikes and Capital Inflows
The rate increases by the US Federal Reserve have caused a flow of international investments into the US Treasury, which has resulted in capital outflows from India.
The US Fed has increased rates by 75 basis points so far this year. This may boost capital flows into developing nations like India.
India's current account deficit is expected to be less than 2% of GDP, which represents a considerable improvement in the country's balance of payments.
Equity capital flows have resumed, and India continues to draw sizable investments in comparison to other developing market counterparts.
Global Standing of India’s Forex Reserves:
Following China, Japan, and Switzerland as the nations having the greatest foreign exchange reserves, India comes in at number four.
Due to a competitive exports market, the majority of nations consistently and significantly sustain big current account surpluses. However, rather than a sizable current account surplus, India, Brazil, and the US have built reserves mostly through capital flows.
RBI’s Strategy for Diversifying Forex Reserves:
The RBI wants to internationalise the Indian rupee in order to lessen dependency on foreign currencies.
The RBI is looking at the possibility of using the rupee and other currencies from Asian Clearing Union members for internal transactions.
The rupee may be used as a designated foreign currency thanks to a deal with the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, encouraging trade between the two nations and enabling rupee transactions for Indian visitors visiting Sri Lanka.
Conclusion:
India's foreign exchange reserves have fluctuated as a result of a number of causes, but the nation's persistent attempts to diversify and enhance its reserves position show that the RBI is taking a proactive stance.
Future improvements to the FX reserve management system might be attributed to the continuous efforts to draw foreign investment and efforts to internationalise the rupee.
Source: The Hindu
Manual Scavenging
GS Paper I (Indian Society)
Context: A substantial number of districts have yet to report themselves as being free of manual scavenging, according to the Social Justice Ministry, even though 530 districts have done so.

Manual Scavenging in India:
The activity of manually collecting human waste from septic tanks or sewers is known as manual scavenging.
The Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013 (PEMSR) outlawed the practise in India.
Human excreta cannot be physically cleaned, carried, disposed of, or handled in any other way until it is disposed of, according to the Act.
The term "manual scavengers" was further expanded in 2013 to cover anyone hired to clean septic tanks, ditches or railway lines.
As a "dehumanising practise," manual scavenging is acknowledged by the Act, which also notes the need to "correct the historical injustice and indignity suffered by the manual scavengers."
Reasons for its persistence:
Marginalised groups in society frequently engage in manual scavenging because they are uninformed of their rights, leaving them open to abuse.
Manual scavenging continues in part due to lax Act enforcement and the exploitation of unskilled labourers.
Municipal officials are discouraged by the high expense of using automated cleaning techniques in sewage systems.
Contractors continue the practise by hiring unskilled workers illegally who are prepared to labour for less money.
The established caste system, with the bulk of manual scavengers being from lower castes, supports the practise.
Various Policy Initiatives:
Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation (Amendment) Bill, 2020: The proposed amendment aims to automate sewage cleaning, give on-site security, and provide financial compensation in the event of sewer-related fatalities.
Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013: This Act forbids all manual faeces cleaning in unhygienic latrines, open drains, or pits, going beyond the limitations on dry latrines.
Rashtriya Garima Abhiyan: The "Maila Mukti Yatra," which was started in 2012, intends to end manual scavenging across the country, beginning in Bhopal.
Prevention of Atrocities Act: Since a sizable portion of manual scavengers are members of the Scheduled Caste, this Act protects sanitation workers.
Compensation: The PEMSR Act and the Supreme Court's ruling in the Safai Karamchari Andolan v. Union of India case require that the families of victims get compensation in the amount of Rs. 10 lakh.
National Commission for Safai Karamcharis (NCSK): The NCSK conducts research on the working conditions of garbage collectors in India and makes suggestions to the government.
NAMASTE Scheme: The NAMASTE programme aims to improve the safety and dignity of sanitation workers by doing away with dangerous sewer and septic tank cleaning methods.
States and UTs with Pending Declaration of Manual Scavenging-Free Districts:
In terms of States and UTs, Jammu and Kashmir, Manipur, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, and Jharkhand have the most districts that have not yet formally proclaimed themselves to be free of manual scavenging.
While states like Bihar, Rajasthan, and Tamil Nadu have declared all of their districts to be free from manual scavenging, several other states and UTs have only claimed 15% to 20% of their districts to be free from the practise.
Way Forward:
Public and municipal authorities must regularly perform surveys and social audits on the use of manual scavengers.
Manual scavengers need to be properly identified and given the tools they need to develop alternative forms of income.
It's important to raise knowledge of the legal protections available to manual scavengers.
Source: The Hindu
Digital Birth Certificates
GS Paper II (Polity & Governance)
Context: Digital birth certificates will be introduced in India under the Registration of Births and Deaths (RBD) Amendment Bill, 2023, which would act as complete papers for a number of important functions.
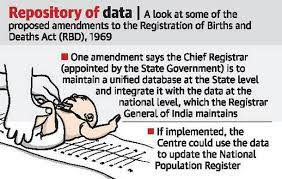
About RBD Bill, 2023:
The Registration of Births and Deaths Act of 1969 is amended.
The Act outlines the rules for controlling birth and death registration.
Key Points from the Bill:
A Registrar General of India must be appointed in order to maintain a national registry of births and deaths. Chief Registrars will also keep state-level databases that are linked to the federal database.
Adoptive parents, biological parents in surrogacy situations, single parents, and unmarried women are now included in the list of those who must furnish Aadhaar data while reporting births.
The proposed Bill aspires to modernise public services by introducing digital registration and electronic distribution of birth and death certificates.
For fatalities that occur on their property, medical institutions are required to give certificates stating the cause of death.
Within seven days of registration, the Registrar must deliver birth and death certificates to the event's registrant.
Within 30 days of receiving the acts or orders, anybody who is unhappy with them may appeal to the District Registrar or Chief Registrar, as appropriate. Within 90 days, a decision on the appeal must be made.
To make registration for adopted, orphaned, abandoned, surrendered, surrogate, and children of single parents or unmarried mothers easier, the Bill aims to gather Aadhaar information.
In order to improve the NPR's efficiency and build the framework for the National Register of Citizens (NRC), the database created through the CRS will also be utilised to update the information for ration cards, property registrations, and ration cards.
Conclusion:
An important step towards improving government operations and public services is India's transition to digital birth certificates.
The nation wants to increase efficiency and transparency in the use of numerous critical services by implementing a centralised system for registration and digital certificate distribution.
Source: Indian Express
Top 10 to Top 3
GS Paper III (Economy)
Context: According to SBI Research experts, India is on track to overtake China as the third-largest economy in the world by FY28, two years earlier than anticipated. The Prime Minister emphasised India's impressive economic growth throughout his administration.

India’s Economic Growth Trajectory:
In comparison to China's growth rate of 84% during the same period, India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increased by an amazing 83% between 2014 and 2023.
India's economy was impacted by the 2008–2009 Global Financial Crisis, although it was substantially more resilient than European nations, giving it a growth edge.
India has surpassed several of the other top 10 economies because they have had difficulty maintaining high growth rates. For instance, during the same nine-year period, the total GDP of the UK increased by just 3%, that of France by 2%, that of Russia by 1%, while Italy's GDP stagnated and Brazil's GDP even shrank by 15%.
India’s Projected Growth:
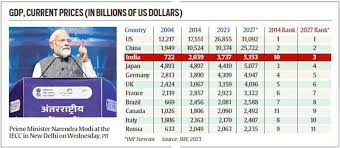
By 2027, India is anticipated to surpass both Japan and Germany to become the third-largest economy in the world, according to projections from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
India's GDP in 2027 will be almost 38% greater than its 2023 level, even with a more modest growth rate of 6% annually.
Only a 15% gain is anticipated for Japan and Germany during the same time span, allowing India to move up to third place.
India's GDP continues to be far behind the top two countries, China and the US.
Positive elements include the economy becoming more digitalized and the chance to attract investments as a result of the unfavourable global perception of China.
Issues with such growth: Per Capita GDP Disparity
Although India's overall GDP growth has been outstanding, per capita GDP data is crucial to understanding the country's residents' true level of affluence.
With a per capita GDP of $2,600, India continues to have the lowest GDP among the top 10 economies and is far behind the nations it has surpassed, such the UK, Brazil, and Italy.
Reasons for such disparity:
MSMEs, which employ 110 million people and account for 30% of India's GDP, have been severely impacted by the epidemic. According to government polls, about 9% of these businesses have reportedly closed as a result of COVID-19.
Core inflation as a result of the decimation of MSMEs has given a few major businesses pricing power and increased expenses for consumers.
India's inability to lower unemployment rates may be attributed in large part to MSMEs' challenges, which push many people to the rural job guarantee programme in search of paid employment.
India's continued struggle to develop a manufacturing-driven economy has an impact on employment generation.
Efforts to alter the labour and land laws to reflect the factor market have been hampered by successive governments.
Conclusion:
The government will need to make consistent efforts to address the hidden crisis, with an emphasis on helping MSMEs and carrying out important reforms.
To move India towards a more secure and inclusive economic future, swift and decisive action is required.
Source: Indian Express
Hematene Nanoflakes
GS Paper III (Science & Technology)
Context: Nanoflakes of hematene, a substance obtained from iron ore, have been found by researchers to be revolutionary. These nanoflakes are proven to exhibit outstanding resistance to and shielding from strong laser irradiance.
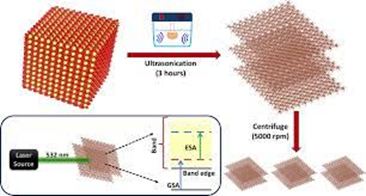
What is Hematene?
Hematite, a common iron mineral, was used to create the unique 2D substance known as hematene.
It is a single-layer, thin material with distinctive qualities that make it promising for a variety of uses, particularly in optics.
Hematene nanoflakes are advantageous for optical limiting applications since they have shown excellent skills in withstanding and shielding against high laser intensity.
Researchers and scientists have developed a keen interest in the material due to its stability and potential for use in cutting-edge technology.
How is it made?
Hematite, which is a naturally occurring mineral form of iron oxide, is converted into hematene via a process that includes sonication, centrifugation, and vacuum-assisted filtering.
It displays increased photocatalysis efficiency while having a thickness of only 3 atoms.
It has magnetic qualities because it is ferromagnetic, like ordinary magnets.
Notably, it has a remarkable capacity for withstanding strong laser intensities and acting as a shield in their presence.
Applications of Hematene Nanoflakes:
Hematene nanoflakes are proven to have remarkable optical limiting properties, making them useful for shielding delicate optical equipment from strong laser energies, such as sensors, detectors, and other optical devices.
Due to its characteristics, hematene may be utilised to create high-performance photodetectors, which are devices that recognise and transform light impulses into electrical signals. There is promise for this use in optical communications, photography, and telecommunications.
Due to its distinct electrical and electrochemical characteristics, hematene can be investigated for uses in energy storage systems like batteries and super-capacitors.
The material's characteristics make it appropriate for optoelectronic devices, such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and photovoltaic cells, which involve the interplay of light and electricity.
Photothermal treatment, a medical procedure that employs light to cure illnesses like cancer, may benefit from hematene's capacity to endure and guard against high laser intensities.
Because of its stability and adaptability to many conditions, hematene may be useful in environmental applications including water purification and pollution management.
The special characteristics of the material may be used to create high-performance sensors for a variety of uses, such as gas detection and environmental monitoring.
The electrical and surface properties of hematene might be investigated for catalytic applications, boosting chemical reactions in many industrial processes.
Source: Indian Express
Facts for Prelims
Women reservation in ULBs in Nagaland:
The Supreme Court demanded explanations from the federal government and the Nagaland government for the failure to implement a women's quota in urban local body (ULB) elections.
The Nagaland Municipal Act of 2001 had previously been updated in 2006 to include a provision for women's reservation in accordance with the 74th constitutional amendment of 1992.
Naga tribal organisations oppose a women's quota in ULBs on the grounds that it violates special rights protected by Article 371(A).
Patriarchal sociocultural norms and tribal customs of the Naga people limit women's ability to make decisions.
Communities added to Schedule Tribe:
The Constitution (Schedule Tribes) Order, 1950 was amended by a bill passed by the Rajya Sabha to add several communities to the list of Chhattisgarh's Schedule Tribes.
Dhanuhar, Dhanuwar, Kisan, Saundra, Saonra, and Binjhia are new communities, as well as three Devanagari iterations of the Pando community.
with accordance with Article 342, the President may inform the STs with reference to any State/UT and, in the case of a State, after consulting with the Governor.
A notice issued by the government may provide a list of STs, which the Parliament may by legislation add to or remove.
Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik (UDAN) 5.2:
Launched by the Minister of Steel and Civil Aviation, UDAN 5.2 is a Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS).
It was started in order to provide connection to the nation's rural and regional communities.
Last-mile connectivity will be accomplished using tiny aircraft like the 1A (9 passengers) and Category 1 (20 seats).
A market-driven programme called UDAN intends to increase regional air connectivity from underserved and unserved airports and lower the cost of air travel.
It was created in accordance with the 2016 National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP) revision.